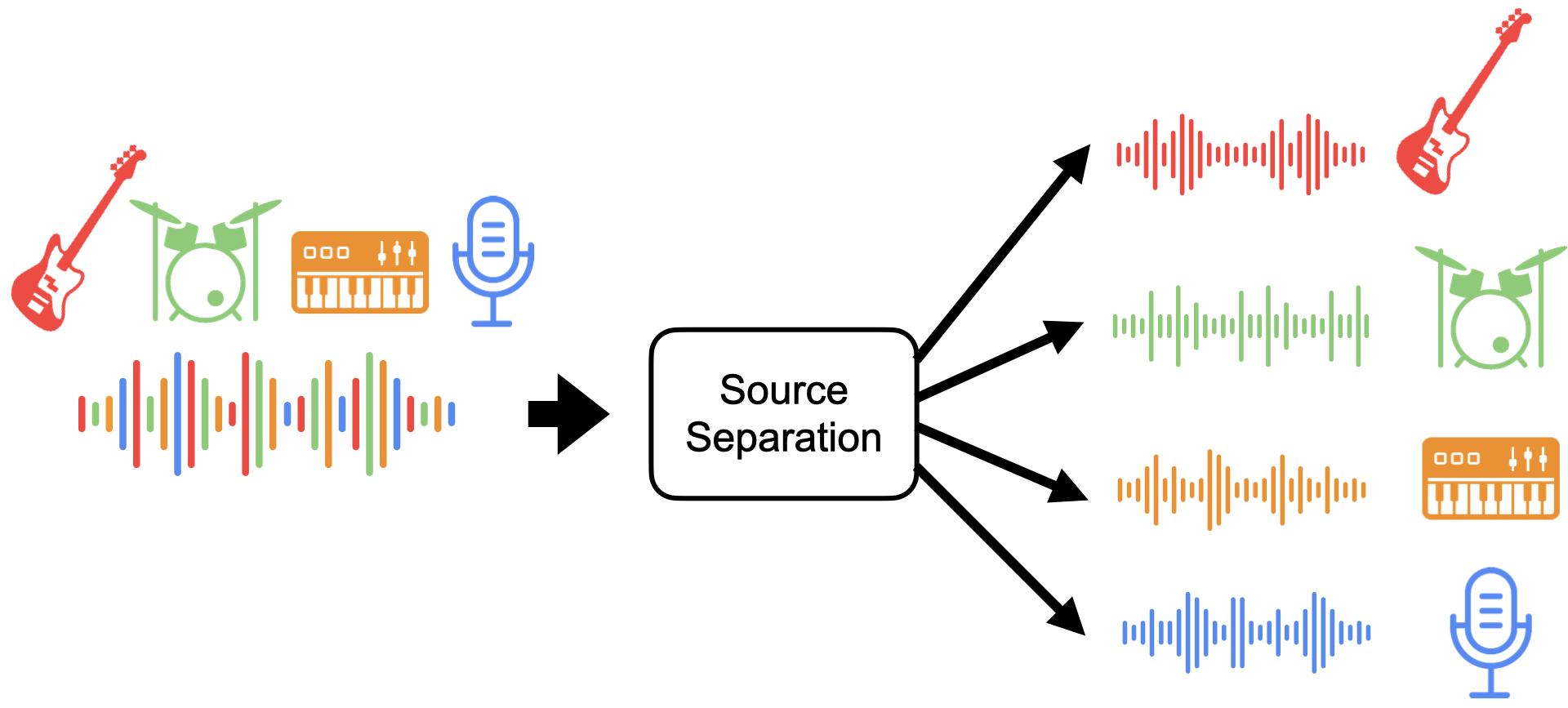
SoundSieve harnesses AI-powered source separation through Demucs to precisely isolate vocals and instruments from audio tracks. Building on techniques used by Spotify and Apple Music, it delivers enterprise-grade audio processing through a scalable, Kubernetes architecture. This enables streaming services, music production studios, and digital platforms to offer enhanced experiences like professional-quality karaoke, remixing tools, and interactive music features. By bringing advanced audio manipulation to the cloud, SoundSieve equips businesses to meet rising demand for AI-driven audio innovation.
This repository implements Music-Separation-as-a-Service (MSaaS), a Kubernetes-based system for waveform source separation. MSaaS provides a REST API for automatic music separation, enabling users to upload MP3 files, process them into separate tracks (vocals, bass, drums, etc.), and retrieve the results.
The project leverages Kubernetes to deploy and manage a microservices architecture that includes:
- REST API service (
rest): Handles API requests for music analysis and communicates with workers via a Redis queue. - Worker service (
worker): Processes MP3 files using Facebook's Demucs, a waveform source separation tool, and stores results in Min.io object storage. - Redis service (
redis): Provides a lightweight database for queuing work requests and logging messages.
The system relies on Min.io for object storage to store uploaded MP3 files and output tracks.
The MSaaS system comprises the following components:
- Redis: Handles the queuing of tasks and logging via
lpush/blpopoperations. - REST API (
rest): Provides endpoints for uploading MP3 files, initiating music separation, and retrieving results. - Worker: Executes the computationally expensive music separation tasks using Demucs.
- Min.io: Stores MP3 files and separated tracks in "queue" and "output" buckets.
Below is architecture/data flow diagram:

Before starting, ensure you have the following:
- Kubernetes Cluster: You can use a local Kubernetes installation or a cloud provider like GKE. For local development, Minikube or Docker Desktop is recommended.
- Min.io: Set up Min.io locally or as a Kubernetes service using the Kubernetes tutorial instructions.
- Redis: Deployed via Kubernetes as a service.
- Docker: Installed locally to build and manage container images.
- Python 3.8+: For running test scripts and interacting with the REST API.
git clone https://github.com/InduVarshini/SoundSieve.git
cd SoundSieve Deploy Min.io locally or on Kubernetes by following the Min.io Kubernetes tutorial. Ensure Min.io is accessible and credentials are correctly configured.
Run the provided script to deploy Redis:
bash deploy-local-dev.sh This also sets up port-forwarding to allow local access to Redis and Min.io services.
Build Docker images for rest and worker:
docker build -t your-dockerhub-user/rest:latest rest/
docker build -t your-dockerhub-user/worker:latest worker/
docker push your-dockerhub-user/rest:latest
docker push your-dockerhub-user/worker:latest Deploy all services using Kubernetes manifests:
kubectl apply -f k8s/redis-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f k8s/minio-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f k8s/rest-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f k8s/worker-deployment.yaml Verify that all pods are running:
kubectl get pods To enable local development, forward Redis and Min.io ports to your localhost:
kubectl port-forward service/redis 6379:6379 &
kubectl port-forward --namespace minio-ns svc/myminio-proj 9000:9000 & The REST API accepts requests for:
- Uploading MP3s
- Processing MP3s
- Retrieving separated tracks
Refer to rest/README.md for endpoint documentation.
Run the provided sample scripts to test the system:
python sample-requests.py
python short-sample-requests.py Monitor logs using the logging service provided in the logs/ directory. Deploy the logs service on Kubernetes or run it locally to view debug messages from the Redis logging queue.
- Redis Deployment: Use
deploy-local-dev.shto deploy Redis with port-forwarding enabled. - REST Server: Develop and test the REST API locally by connecting to Redis and Min.io via
localhost. - Worker Node: Test the worker service locally by connecting to the port-forwarded Redis queue and Min.io.
- Debugging: Use the logging pod to debug issues during development.
- Use short sample MP3 files during development to reduce processing time and memory usage.
- Monitor Kubernetes resource usage with:
kubectl describe node <node-name>
- Use versioned Docker images for better deployment tracking.
- Kubernetes Cheat Sheet
- Demucs: Waveform Source Separation
- Min.io Python API
- CSCI 4253/5253 Kubernetes Tutorial
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.